Sperm vitality, as estimated by assessing the membrane integrity of the cells, may be determined routinely on all samples, but is especially important for samples with less than about 40% progressively motile spermatozoa. The percentage of live spermatozoa is assessed by identifying those with an intact cell membrane, from dye exclusion or by hypotonic swelling. The dye exclusion method is based on the principle that damaged plasma membranes, such as those found in non-vital (dead) cells, allow entry of membrane impermeant stains. The hypo-osmotic swelling test presumes that only cells with intact membranes (live cells) will swell in hypotonic solutions.
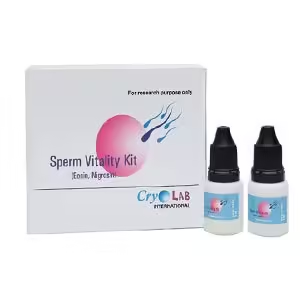
Vitality test using eosin–nigrosin
The staining kit consists of 2X 5 ml stain solutions
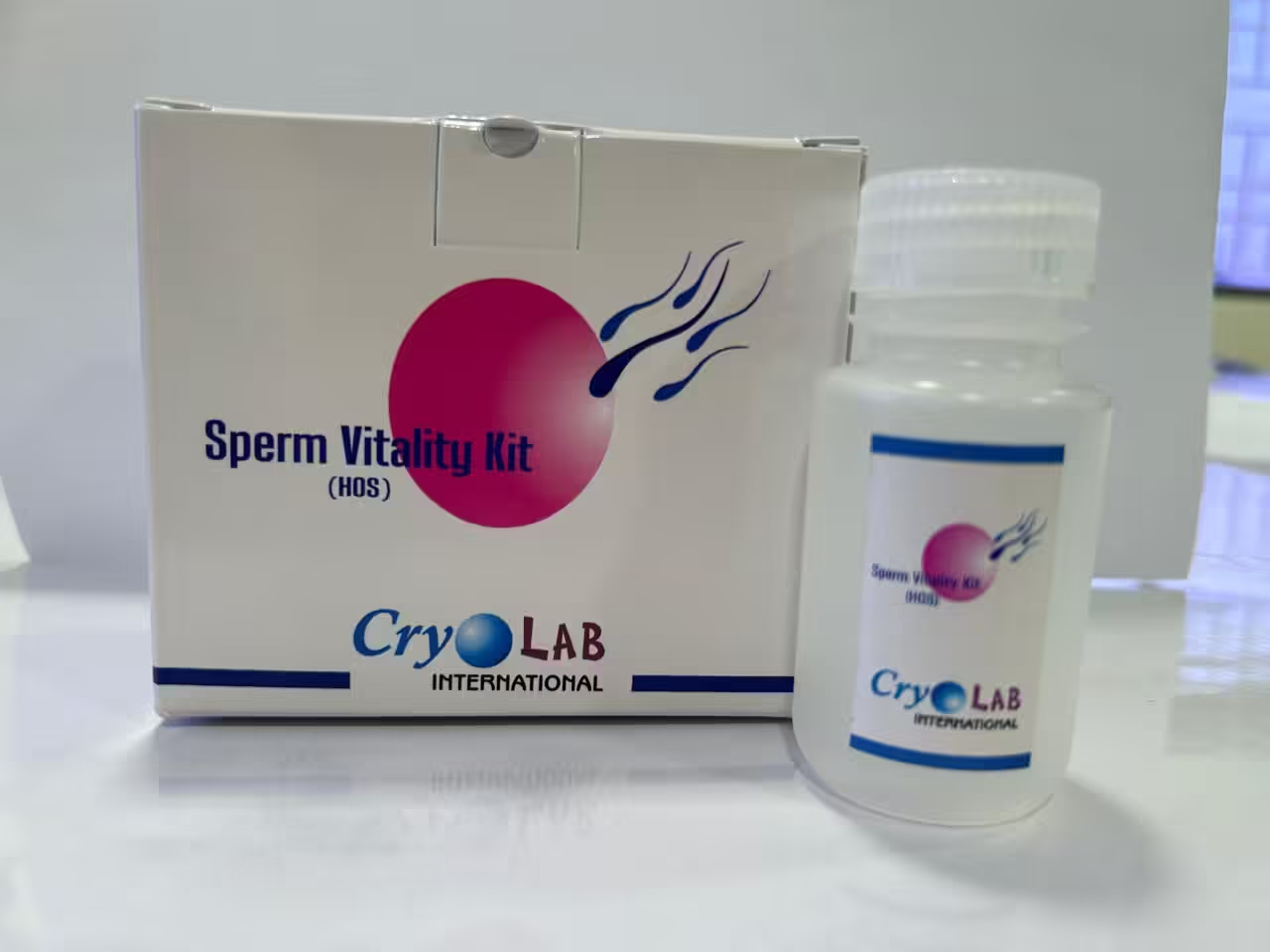
Vitality test using hypo-osmotic swelling.
The kit consists of 50 ml HOS solution